Words and photos from ![]() 4wd talk
4wd talk
The Science of Heat: Understanding the Efficiency of Diesel Heaters
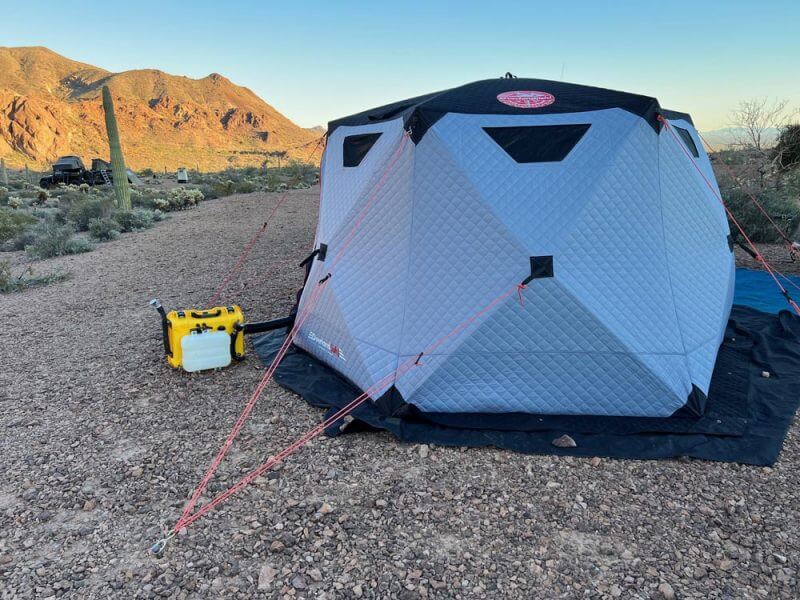

If you follow my articles here on 4WDTalk, you likely already know that I’m a big fan of diesel heaters.
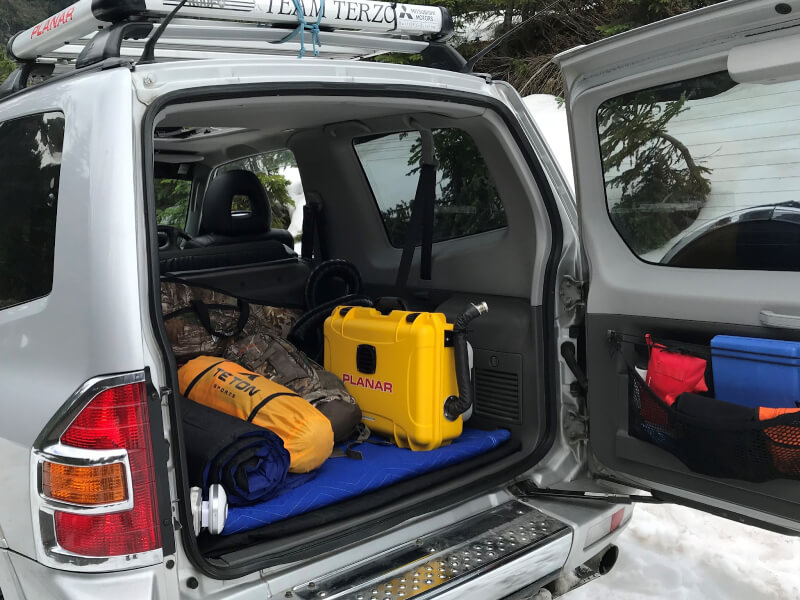
In fact, I have a 2kw Autoterm diesel air heater installed in the nose of my Turtleback Expedition Trailer, and I also have a 4kw Planar Heaters portable diesel heater that I bring along for heating up any ground tents that I use.
But the question is, why do I like diesel heaters?
Well, let’s go beyond the “they work great” argument and explore the science of how diesel heaters work compared to electric and propane heaters.
Let’s get started!
Understanding Thermodynamics in Heating Systems
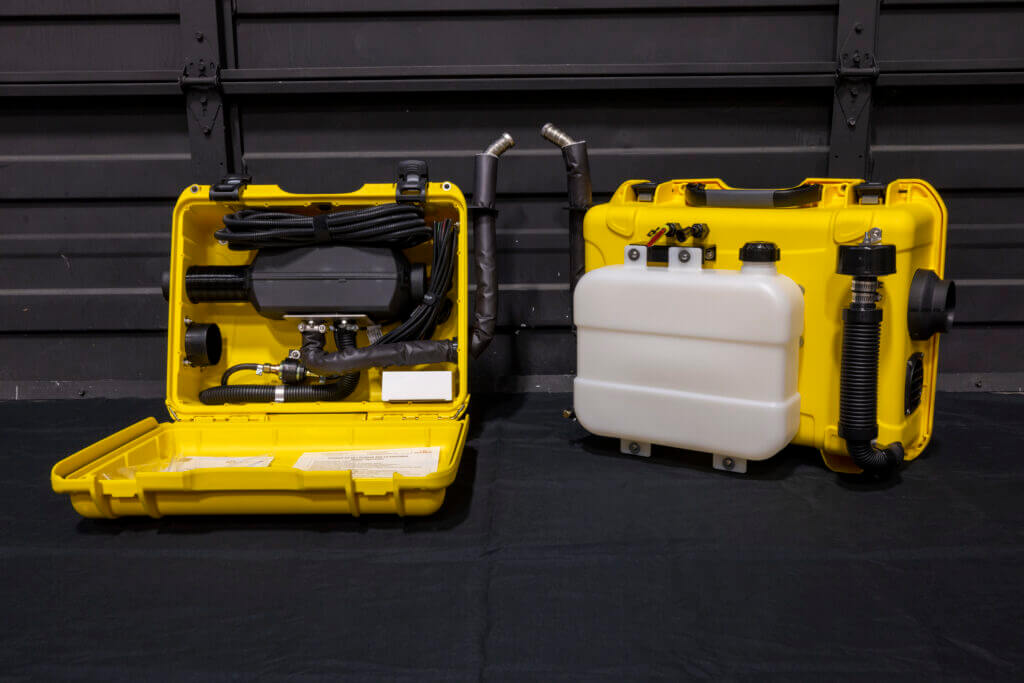
In heating systems, the principles of thermodynamics play a pivotal role, illustrating how energy is conserved, transferred, and transformed. The core idea is that energy cannot be created nor destroyed but can only change from one form to another.
For instance, in portable diesel heaters like the ones from Planar Heaters shown above, the chemical energy in diesel fuel is converted into thermal energy through combustion. This process is highly efficient due to diesel’s inherent energy-rich composition and the effective combustion process, which minimizes energy loss and maximizes heat production.
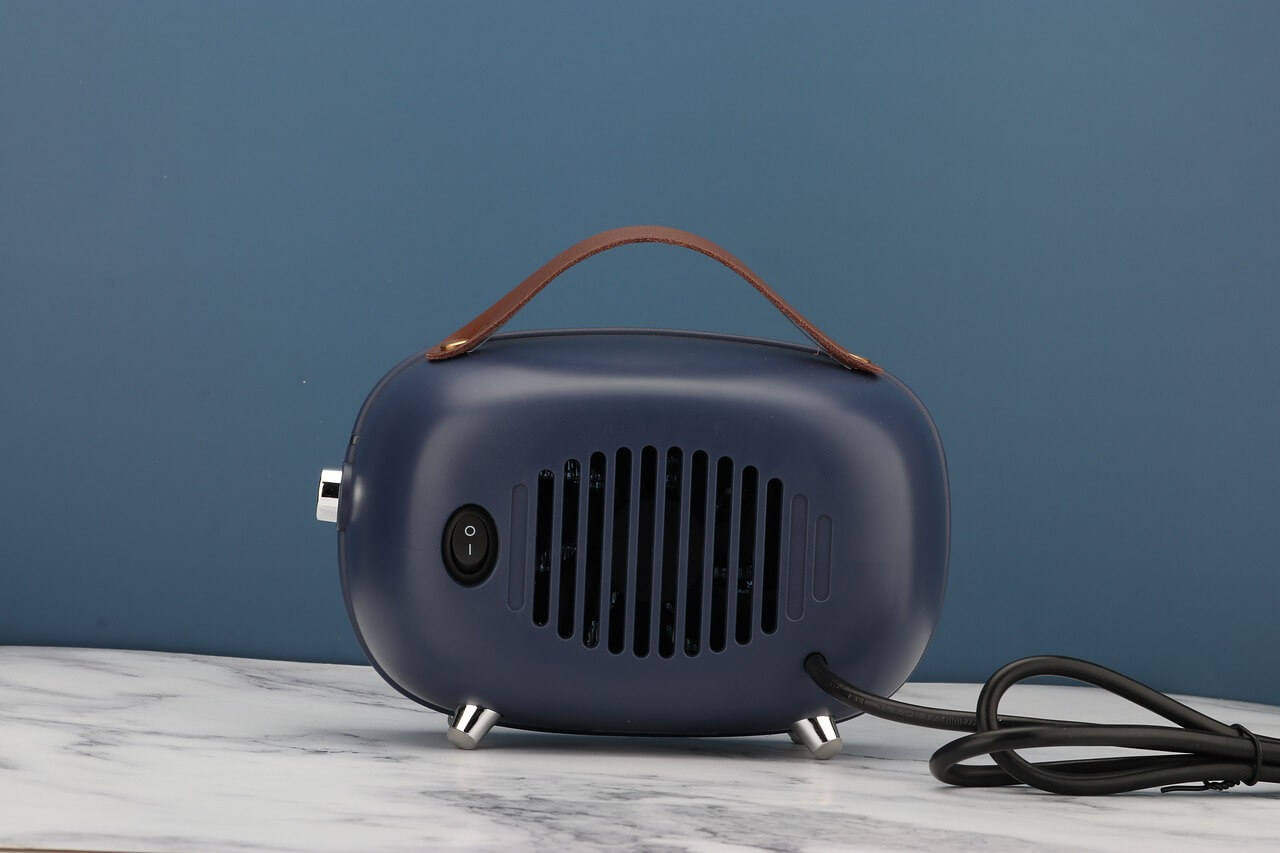

On the other hand, electric heaters like the one shown above convert electrical energy into thermal energy by passing an electric current through a resistive element, which then radiates heat. While this process is also efficient, the overall efficiency may be lower due to losses in electricity generation and transmission.
Propane heaters operate similarly to diesel heaters, where the chemical energy in propane is converted into thermal energy through combustion. However, the combustion process and the energy content of propane can be less efficient compared to diesel, leading to potentially more energy loss and less heat production.
Through understanding these thermodynamic processes, one can better appreciate the efficiency variances among diesel, electric, and propane heating systems, showcasing how the inherent properties and combustion mechanisms of diesel fuel make diesel heaters a more efficient choice for heat generation.
Fuel Efficiency

The energy content of a fuel, often measured in British Thermal Units (BTU) or Joules, is a critical determinant of its efficiency as it signifies the amount of heat energy that can be derived from the fuel.
Diesel fuel is known for its high energy content, boasting about 130,000-140,000 BTU per gallon. This is significantly higher when compared to propane, which has around 91,500 BTU per gallon, and electricity, which provides about 3,412 BTU per kilowatt-hour. The higher energy content of diesel means that for a given volume of fuel, diesel heaters can produce more heat, making them inherently more efficient.
The efficiency of diesel heaters is further amplified through the combustion process. Diesel combustion occurs at higher temperatures and under higher pressure, which ensures a more complete combustion, translating into less wasted fuel and more generated heat. This contrasts with the combustion process in propane heaters, which may not achieve the same level of combustion efficiency, and electric heaters, which are dependent on the efficiency of electricity generation and transmission, often laden with energy losses.
Moreover, diesel heaters can retain heat for longer due to their design and the materials used, which can further optimize fuel efficiency by reducing the need for continuous fuel combustion. Therefore, the high energy content of diesel fuel, coupled with efficient combustion and heat retention characteristics, positions diesel heaters as a more fuel-efficient option when compared to electric and propane alternatives.
Diesel Heater Combustion Efficiency
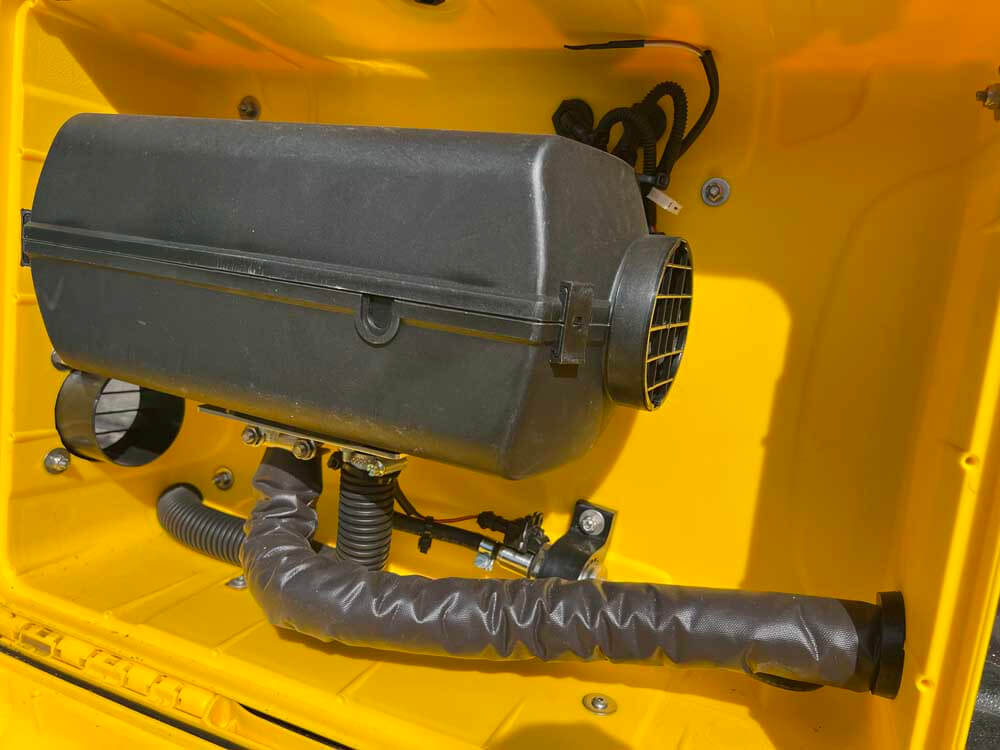

The efficiency of combustion in heating systems largely depends on the completeness of the combustion process and the effective transfer of the generated heat. Diesel combustion is known for its efficiency, often outperforming propane. The inherent properties of diesel fuel, such as its higher energy density and higher autoignition temperature, contribute to a more complete combustion process. Unlike propane, diesel fuel has a longer ignition delay which allows more time for the fuel-air mixture, leading to better combustion efficiency.
The design of diesel heaters plays a crucial role in maximizing combustion efficiency and heat transfer.
Diesel heaters often incorporate advanced combustion chambers that ensure optimal air-fuel mixing and complete combustion. The combustion chambers are engineered to withstand higher temperatures and pressures, further promoting efficient combustion.
Furthermore, diesel heaters are usually equipped with high-quality heat exchangers that effectively capture and distribute the generated heat. The use of high-grade materials in these heat exchangers minimizes heat loss and ensures a more efficient heat transfer process.
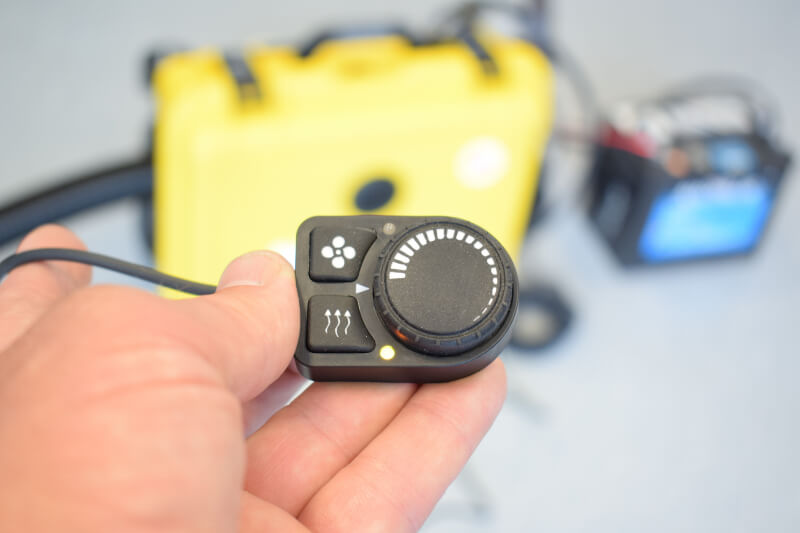

Moreover, modern diesel heaters often incorporate smart control systems and sensors that optimize the combustion process based on real-time performance data (some also offer remote controls, like my portable diesel heater from Planar Heaters). This level of control not only enhances combustion efficiency but also helps in maintaining consistent heating, making diesel heaters a reliable choice.
Through a combination of superior fuel properties, sophisticated design, and smart control systems, diesel heaters are able to offer better combustion efficiency and effective heat transfer, making them a highly efficient heating solution compared to propane alternatives.
Heat Retention
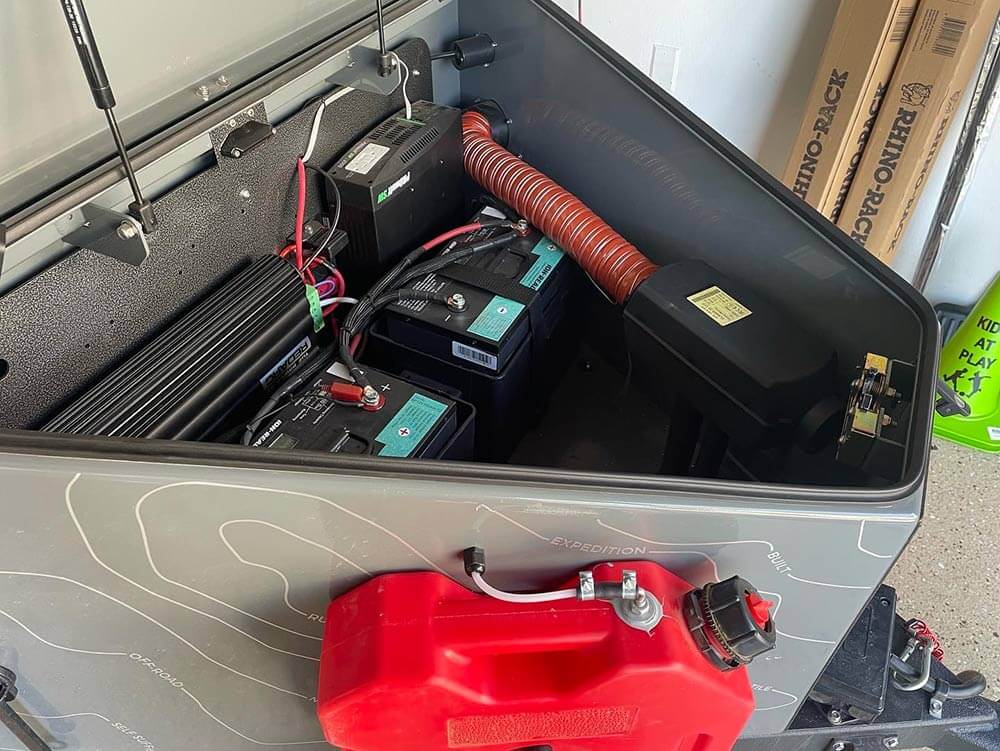

The efficiency of a heating system also significantly hinges on its ability to retain heat and minimize heat loss, ensuring that the generated heat is effectively utilized for warming the intended space. Diesel heaters often excel in this aspect due to a combination of materials used and design features incorporated.
Materials
Diesel heaters typically utilize materials with excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties.
For instance, the use of stainless steel and other high-grade metals in the construction of the combustion chamber and heat exchanger ensures that heat is effectively captured and transferred. Additionally, the insulation materials used in diesel heaters are designed to minimize heat loss, ensuring that the heat remains within the system or is directed to the intended spaces, rather than dissipating into the surrounding environment.
Design Features
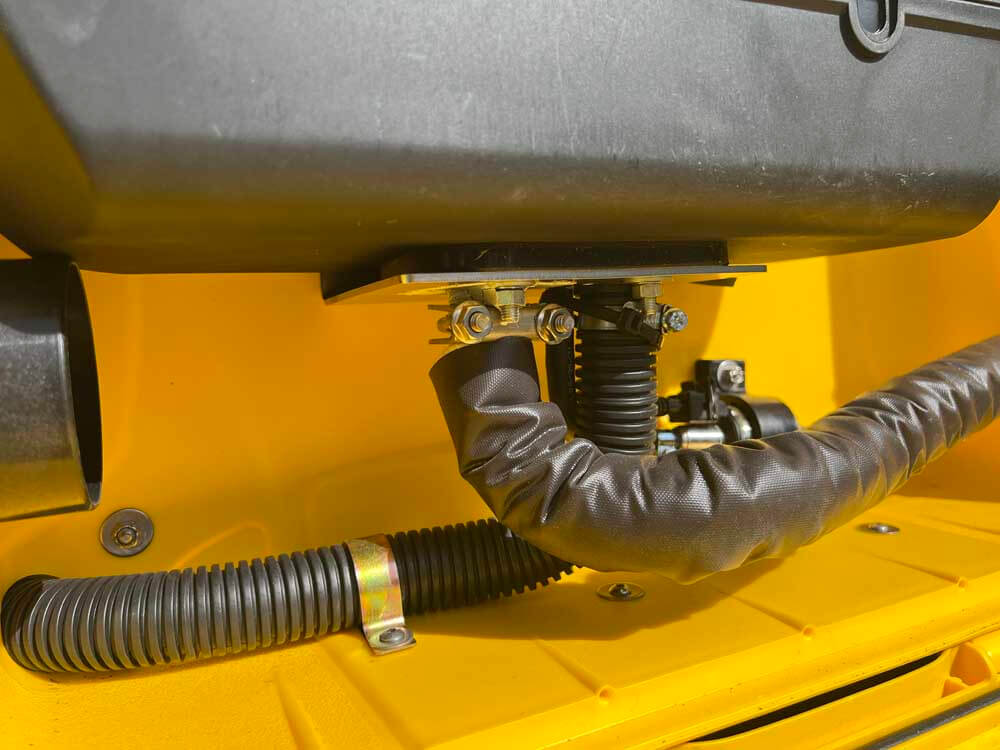

Diesel heaters often feature design enhancements aimed at maximizing heat retention. For instance, the design of the combustion chamber and heat exchanger in a diesel heater is optimized to ensure a thorough heat transfer process, capturing the maximum amount of heat generated from the combustion of diesel fuel. Moreover, the routing of exhaust gasses is engineered to recover residual heat that would otherwise be lost, further improving the efficiency of the heater.
Furthermore, modern diesel heaters may incorporate advanced sealing techniques to prevent heat leaks, and well-designed venting systems to direct the heat effectively. They may also feature variable speed fans and smart controls that optimize the distribution of heat based on the current needs and conditions, ensuring efficient heat retention and utilization.
The meticulous attention to materials and design in diesel heaters significantly contributes to their superior heat retention capabilities and less heat loss when compared to other heating alternatives. Through reducing heat loss and maximizing heat retention, diesel heaters ensure that the energy from the fuel is effectively utilized, enhancing their overall heating efficiency.
Comparative Analysis: Diesel vs Electric vs Propane Heaters
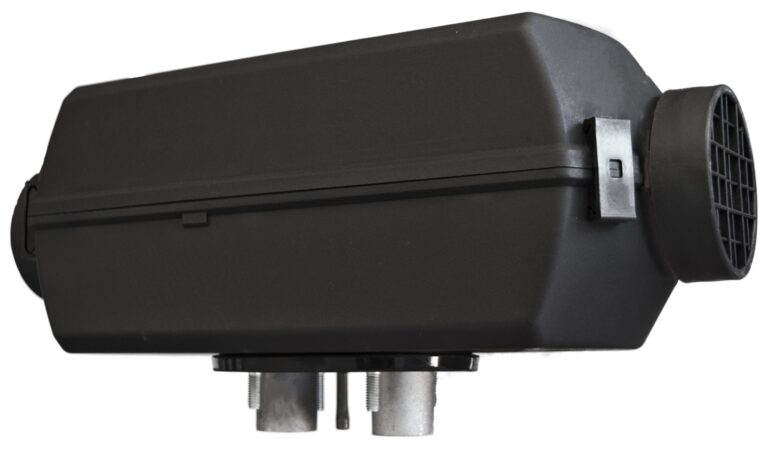

When comparing the efficiency, cost of operation, and environmental impact of diesel heaters, electric heaters, and propane heaters, several factors come into play.
Efficiency of Diesel, Electric, and Propane Heaters
Electric heaters are highly efficient at converting electricity into heat, with efficiency rates close to 100%. They provide instant and precise heating, making them a suitable choice for smaller spaces or spot heating.
Diesel heaters are less efficient than electric heaters, as they rely on combustion to generate heat. This process can result in energy losses and lower overall efficiency. Meanwhile, propane heaters fall between electric and diesel heaters in terms of efficiency. They produce heat by burning propane gas, which is more efficient than diesel combustion but may not be as precise as electric heating.
Cost of Operation of Diesel, Electric, and Propane Heaters
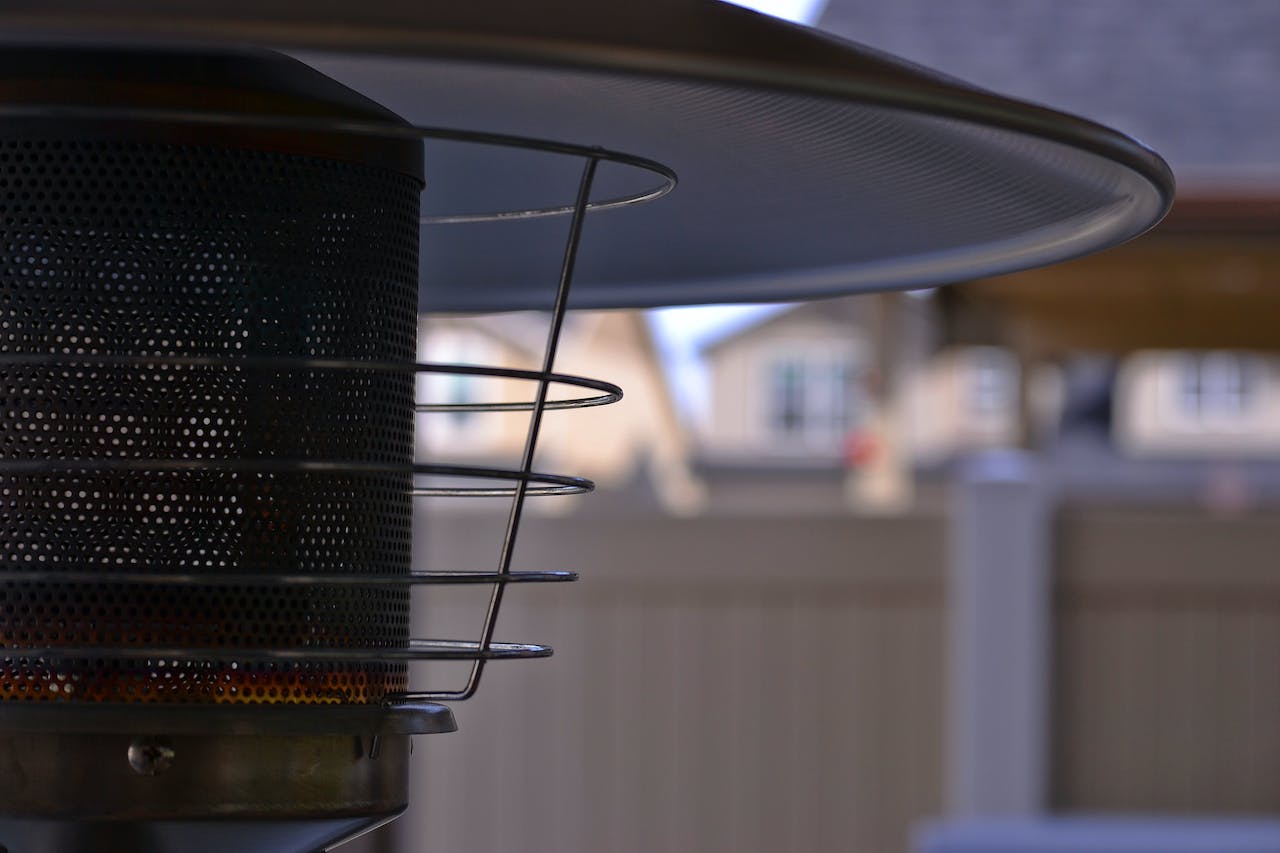

Electric heaters tend to have higher operating costs due to the cost of electricity. In regions with expensive electricity rates, running electric heaters can be a significant expense over time.
Diesel heaters can be more cost-effective in terms of fuel costs, as diesel fuel is often less expensive than electricity. However, the initial setup cost, including fuel storage and maintenance, can be higher.
Propane heaters usually offer a balance between fuel cost and efficiency, making them a cost-effective option for many users. Propane is typically more affordable than electricity, and the heaters themselves are often more economical than electric and diesel options.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Diesel Heater Efficiency
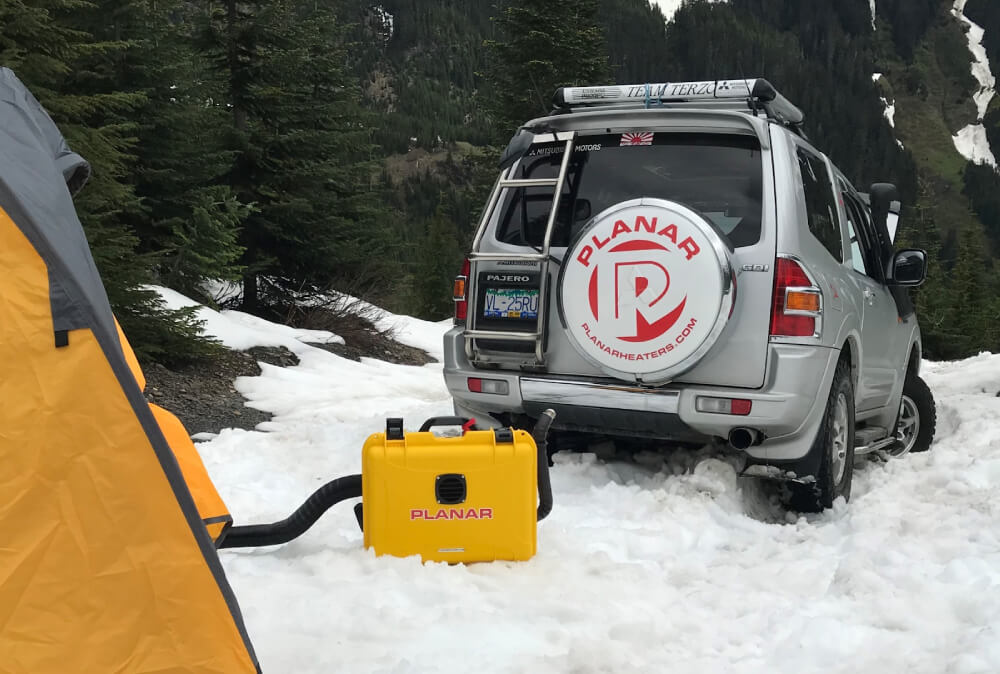

Diesel heaters’ efficiency extends beyond camping, overlanding, and industrial settings into various other real-world scenarios. In the transportation sector, for instance, diesel-powered heaters are used in many long-haul trucks and buses to provide cabin heating during cold winter months.
These heaters are renowned for their quick warm-up times and fuel efficiency, ensuring a comfortable environment for drivers and passengers without overburdening the vehicle’s fuel consumption. This translates to significant savings for fleet operators, making diesel heaters a smart choice for maintaining both comfort and cost-effectiveness on the road.

Another compelling case study emerges in the context of emergency response and disaster relief efforts. In situations where immediate heating is critical, such as in the aftermath of natural disasters or during humanitarian missions in remote areas, diesel heaters offer a reliable solution.
Their ability to run on readily available diesel fuel and produce high levels of heat ensures that critical spaces like field hospitals or emergency shelters can be quickly heated, enhancing the well-being of those affected. The fuel’s extended shelf life and relative ease of storage make diesel heaters particularly suitable for disaster scenarios, where electric or propane alternatives may be less feasible due to logistical challenges or limited resources.

Additionally, in the agricultural sector, diesel heaters are often employed for various applications, including greenhouse heating and crop drying. These heaters are prized for their exceptional fuel efficiency, ensuring that farmers can maintain optimal growing conditions and protect their crops from frost during the colder months.
The cost-effectiveness of diesel heaters in this context, along with their durability and adaptability to the agricultural environment, underscores their efficiency compared to electric and propane alternatives. In other words, diesel heaters have repeatedly proven their advantages in a diverse range of real-world scenarios – camping and overlanding included – and offer superior efficiency and performance across various industries and applications.
Conclusion: Diesel Heaters for the Win!

In conclusion, the efficiency of diesel heaters stands out as a significant advantage in the realm of heating systems. Understanding the principles of thermodynamics and energy conservation, it becomes evident that diesel heaters are a highly efficient choice for heat generation. This efficiency arises from a combination of factors, starting with the inherent energy-rich composition of diesel fuel and the effective combustion process, which minimizes energy loss and maximizes heat production.
Moreover, the energy content of diesel fuel, measured in BTUs, surpasses that of propane and electricity, allowing diesel heaters to produce more heat for a given volume of fuel.
The efficiency of combustion in diesel heaters is further enhanced by their design, featuring advanced combustion chambers that ensure optimal air-fuel mixing and complete combustion. Additionally, the incorporation of high-quality heat exchangers and smart control systems optimizes the distribution of heat, making diesel heaters both efficient and reliable.
Furthermore, the exceptional heat retention capabilities of diesel heaters, attributed to the use of materials with excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties, ensure that the energy from the fuel is effectively utilized, reducing heat loss and enhancing overall heating efficiency.
In comparison to electric and propane heaters, diesel heaters consistently demonstrate their fuel efficiency and heat production capabilities across various real-world scenarios, including transportation, emergency response, and agriculture. This efficiency not only conserves energy but also translates into cost savings and reliability.
So, in short, diesel heaters excel in terms of both energy conservation and cost efficiency, making them a preferred choice for heating needs in a wide range of applications. It’s my preferred method of heating my various tents because the reliability of my diesel heaters from Autoterm and Planar has been proven time and time again. When you head way off the grid for your camping adventures, that’s exactly what you want – reliable service from your heat source!





